
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Prediabetes Progression and Regression on Objectively- Measured Physical Function: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Yiming Zhu, Bo Xie, Wenji Chen, Duolao Wang, Xue Cai, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):859-868. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0377
- 1,376 View
- 124 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prediabetes leads to declines in physical function in older adults, but the impact of prediabetes progression or regression on physical function is unknown. This study assessed this longitudinal association, with physical function objectivelymeasured by grip strength, walking speed, and standing balance, based on the Health and Retirement Study enrolling United States adults aged >50 years.
Methods
Participants with prediabetes were followed-up for 4-year to ascertain prediabetes status alteration (maintained, regressed, or progressed), and another 4-year to assess their impacts on physical function. Weak grip strength was defined as <26 kg for men and <16 kg for women, slow walking speed was as <0.8 m/sec, and poor standing balance was as an uncompleted fulltandem standing testing. Logistic and linear regression analyses were performed.
Results
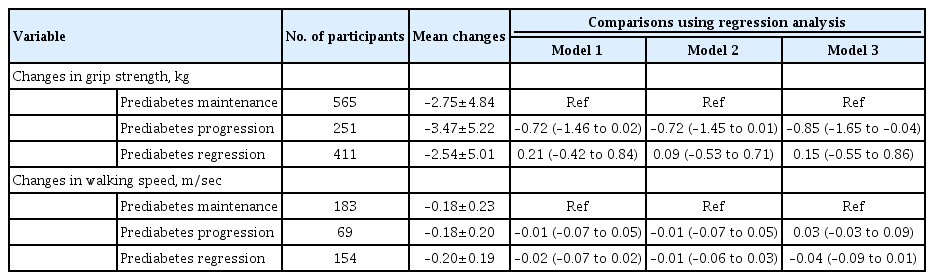
Of the included 1,511 participants with prediabetes, 700 maintained as prediabetes, 306 progressed to diabetes, and 505 regressed to normoglycemia over 4 years. Grip strength and walking speed were declined from baseline during the 4-year followup, regardless of prediabetes status alteration. Compared with prediabetes maintenance, prediabetes progression increased the odds of developing weak grip strength by 89% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.04 to 2.44) and exhibited larger declines in grip strength by 0.85 kg (95% CI, –1.65 to –0.04). However, prediabetes progression was not related to impairments in walking speed or standing balance. Prediabetes regression also did not affect any measures of physical function.
Conclusion
Prediabetes progression accelerates grip strength decline in aging population, while prediabetes regression may not prevent physical function decline due to aging.

 KDA
KDA First
First Prev
Prev





